LAN topologies define the manner in which network devices are organized. Four common LAN topologies exist:
- A bus topology is a linear LAN architecture in which transmissions from network stations propagate the length of the medium and are received by all other stations. Many nodes can tap into the bus and begin communication with all other nodes on that cable segment. A break anywhere in the cable will usually cause the entire segment to be inoperable until the break is repaired. Of the three most widely used LAN implementations, Standard Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 networks implement a bus topology in which all devices are connected to a central cable, called the bus or backbone.
- A ring topology is a LAN architecture in which all devices are connected to one another in the shape of a closed loop, so that each device is connected directly to two other devices, one on either side of it. Both Token Ring/IEEE 802.5 and FDDI networks implement a ring topology.
- A star topology is a LAN architecture in which the endpoints on a network are connected to a common central hub, or switch, by dedicated links. 10BaseT Ethernet uses a star topology, generally with a computer being located at one end of the segment, and the other end being terminated with a hub. The primary advantage of this type of network is reliability – if one point-to-point segments has a break, it will only affect the nodes on that link; other computer users on the network continue to operate as if that segment were non-existent.
- A tree topology is a LAN architecture that is identical to the bus topology, except that branches with multiple nodes are possible in this case.
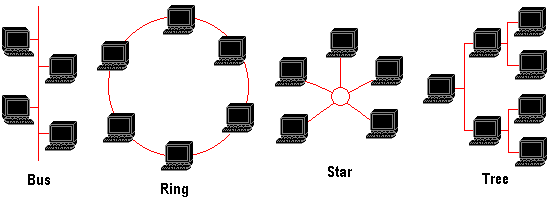
These topologies are logical architectures and the way in which devices are physically organized can mix topologies. For example, a star-wired bus network – as used by 10BaseT Ethernet – typically consists of a high-bandwidth backbone bus which connects to a collection of slower-bandwidth star segments.
These topologies are logical architectures and the way in which devices are physically organized can mix topologies. For example, a 10BaseT network’s use of a hub effectively transforms a standard bus topology to a star-wired bus topology. A network comprising a high-bandwidth backbone bus which connects to a collection of slower-bandwidth star segments is another common example of this type of mixed topology.
Of the three most widely used LAN implementations, both Fibre Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) and Token Ring/IEEE 802.5 networks implement a ring topology and Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 networks implement a bus topology.
- OSI Model
- Network Topologies
- FDDI Networking
- Token Ring Networks
- Ethernet
- Fast Ethernet
- Gigabit Ethernet
- Peer to Peer Network Architecture
- Client/Server Architecture
- P2P Networking
- Network Hardware
- NIC Cards
- Hubs and Repeaters
- Bridges
- Routers
- Network Switches
- Network Transceivers
- Cabling
- Home Networking
- Ethernet Networks
- Phone-line Networks
- Power-line Networks
- IEEE 802.11
- Wireless Networks
- Technology Comparison