 You can record from any analogue audio device that provides line-out terminals. Some analogue audio devices can be connected directly to your computer’s sound card.
You can record from any analogue audio device that provides line-out terminals. Some analogue audio devices can be connected directly to your computer’s sound card.
However, the usual method for transferring material from vinyl LP is to connect the analogue audio device to a stereo pre-amp and then connect the pre-amp to your computer’s sound card.
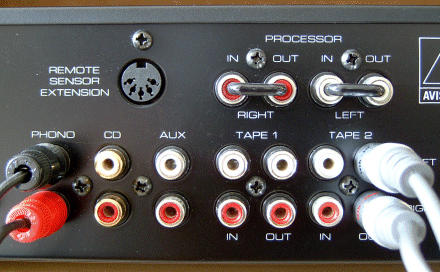
Oftentimes this will be via a Tape-Out connector, which delivers a 1v peak-to-peak voltage signal which the line-in input of a sound card is designed to accept.
If you have an Auxiliary connector, that would do equally well.
Most PC soundcards utilise a 3.5mm (1/8-in) jack as the line input connector and most hi-fi equipment uses RCA type sockets for connecting audio components.
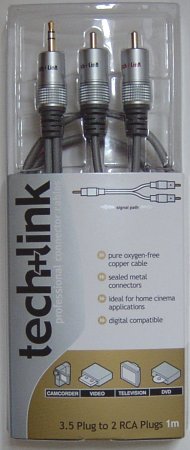
The cable options are therefore:
- A Y connector, with two RCA plugs at one end and a single, stereo 3.5mm minijack at the other (also called a stereo RCA-to-headphone cable).
- A stereo hook-up cable with two pairs of RCA-style, left- and right-channel connectors (male), and an audio adapter with a pair of RCA-style, left- and right-channel connectors (female) and a single line-in, 3.5mm minijack.
Note how the metal part of a stereo jack is divided with an insulator between the left and right channels.
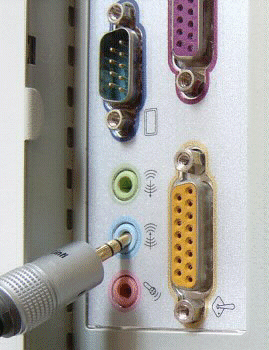
Connect this to your PC’s sound card.
The various sockets will either be marked in text or with symbols. In the case of the latter, the Line-in is denoted by a small set of concentric circles with an arrow pointing into the centre.