Test – Originally scheduled to be available concurrently with the Pentium III processor in the spring of 1999, Intel’s much delayed 820 chipset was finally launched in November that year. Those delays – which had left Intel in the position not having a chipset that supported the 133MHz system bus speed their latest range of processors were capable of – were largely due to delays in the production of Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM), a key component in Intel’s 133MHz platform strategy.
Direct RDRAM memory provides a memory bandwidth capable of delivering 1.6 GBps of maximum theoretical memory bandwidth – twice the peak memory bandwidth of 100MHz SDRAM systems. Additionally, the 820’s support for AGP 4x technology allows graphics controllers to access main memory at more than 1 GBps – twice that of previous AGP platforms. The net result is the significantly improved graphics and multimedia handling performance expected to be necessary to accommodate future advances in both software and hardware technology.
The 820 chipset employs the Accelerated Hub Architecture that is offered in all Intel 800 series chipsets – the first chipset architecture to move away from the traditional Northbridge Southbridge design. It supports a bandwidth of 266 MBps and, with it’s optimized arbitration rules which allow more functions to run concurrently, delivers significantly improved audio and video handling. The chipset’s three primary components are:
- Memory Controller Hub
- I/O Controller Hub, and
- Firmware Hub.
The Memory Controller Hub provides a high-performance interface for the CPU, memory and AGP and supports up to 1GB of memory via a single channel of RDRAM using 64-, 128- and 256-Mbit technology. With an internal bus running at 1.6 GBps and an advanced buffering and queuing structure, the Memory Hub Controller balances system resources and enables concurrent processing in either single or dual processor configurations.
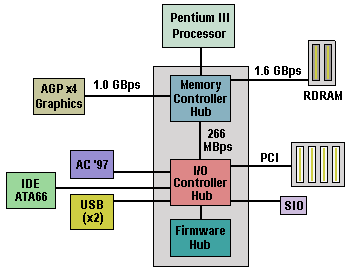
The I/O Controller Hub forms a direct connection from the PC’s I/O devices to the main memory. This results in increased bandwidth and significantly reduced arbitration overhead, creating a faster path to main memory. To capitalise further on this faster path to main memory, the 820 chipset features an integrated AC97 controller in addition to an ATA66 drive controller, dual USB ports and PCI add-in cards.
The Firmware Hub stores system and video BIOS and includes a first for the PC platform – a hardware-based random number generator. The Intel RNG provides truly random numbers through the use of thermal noise – thereby enabling stronger encryption, digital signing and security protocols. This is expected to be of particular benefit to the emerging class of e-commerce applications.
The i820 hadn’t long been on the market before Intel – recognizing that the price of RDRAM was likely to remain high for sometime – designed and released an add-on chip, the 82805 Memory Translator Hub (MTH), which, when implemented on the motherboard, allowed the use of PC100 SDRAM. Sitting between the i820’s Memory Controller Hub (MCH) and the RDRAM memory slots, the MTH chip translates the Rambus memory protocol that’s used by RDRAM into the parallel protocol required by SDRAM, thereby allowing the i820 to use this much more price attractive memory.
Within a few months, a bug in the MTH component came to light. This was serious enough to cause Intel to recall all MTH-equipped i820-motherboards. Since it wasn’t possible to replace the defective chip Intel took the extraordinary step of giving every owner of an MTH-equipped i820 motherboard a replacement non-MTH motherboard as well as RDRAM to replace the SDRAM that was used before!
- Intel’s Triton Chipsets Explained – their history, architecture and development
- Intel 440 Chipsets – 440LX, 440EX, 440BX, 440ZX, 440GX
- i810 Chipset
- Intel 820 Chipset
- i815 Chipsets
- i850 Chipsets
- i845 Chipset
- What is the Intel E7205 Chipset? What Features Does it Have?
- i875P Chipset
- i865 Chipsets
- What is Intel’s 925X PCI Express Chipset
- i915 Chipset
- i945 Chipset
- Intel’s 955X Express Chipset – Glenwood
- i965 Chipset
- A Comparison Chart of Intel’s Chipsets from 915P to P965