The Pentium’s CISC-based architecture represented a leap forward from that of the 486. The 120MHz and above versions have over 3.3 million transistors, fabricated on a 0.35-micron process. Internally, the processor uses a 32-bit bus but externally the data bus is 64 bits wide. The external bus required a different motherboard and to support this Intel also released a special chipset for linking the Pentium to a 64-bit external cache and to the PCI bus.
The majority of Pentiums (75MHz and above) operate on 3.3v with 5v I/O protection. The Pentium has a dual pipelined superscalar design, allowing it to execute more instructions per clock cycle. There are still five stages (Prefetch, Instruction Decode, Address Generate, Execute and Write Back) in the execution of integer instructions, like that of the 486, but the Pentium has two parallel integer pipelines, enabling it to read, interpret, execute and despatch two operations simultaneously. These only handle integer calculations – a separate Floating Point Unit handles real numbers.
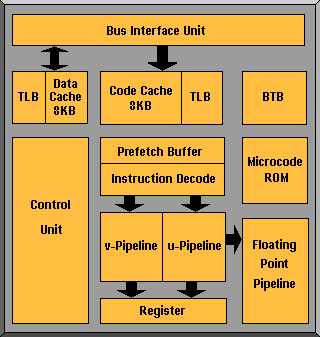
The Pentium also uses two 8KB, two-way set, associative buffers (also known as primary or Level 1 cache), one for instructions and another for data. This is twice the amount of its predecessor, the 486. These caches contribute to increased performance because they act as a temporary storage place for data instructions obtained from the slower main memory.
A Branch Target Buffer (BTB) provides dynamic branch prediction. The BTB enhances instruction execution by remembering which way an instruction branched and applying the same branch the next time the instruction is used. When the BTB makes a correct prediction, performance is improved. An 80-point Floating Point Unit provides the arithmetic engine to handle real numbers. A System Management Mode (SMM) for controlling the power use of the processor and peripherals rounds out the design.
The table below shows the various incarnations of the Pentium processor from its launch in 1993 up until the introduction of the Pentium MMX:
| Date | Codename | Transistors | Fabrication (µm) | Speed (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | P5 | 3,100,000 | 0.80 | 60/66 |
| 1994 | P54 | 3,200,000 | 0.50 | 75/90/100/120 |
| 1995 | P54 | 3,300,000 | 0.35 | 120/133 |
| 1996 | P54 | 3,300,000 | 0.35 | 150/166/200 |
- Pentium Architecture
- Pentium Pro
- Pentium MMX Technology
- Pentium II
- Pentium SEC
- Pentium “Deschutes
- Pentium Xeon
- Pentium III
- Pentium Tualatin
- Pentium 4
- Pentium Northwood
- Hyper-Threading Technology
- Pentium Prescott
- Pentium Processor Numbers
- Multi-Core Processors
- Pentium Smithfield
- Pentium D
- Pentium Roadmap