Intel’s NLX design, introduced in 1997, is an improvement on the LPX design for low-profile systems, with an emphasis on ease of maintenance. The NLX format is smaller, typically 8.8in wide by 13in long, so well suited for low-profile desktop cases.
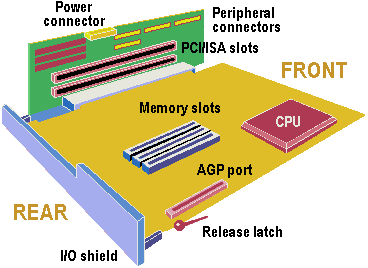
All expansion slots, power cables and peripheral connectors are located on an edge-mounted riser card, allowing simple removal of the main motherboard, which is mounted on rails in the chassis. It uses a full-width I/O shield to allow for different combinations of rear-panel I/O. The design allows for use of an AGP card, but the slot must be on the motherboard, which reduces the ease of maintenance when such a card is implemented.
- Evolution of the motherboard
- BIOS – What motherboard BIOS does for a PC
- CMOS – complementary metal oxide silicon – RAM chips on motherboards
- EFI – Extensible Firmware Interface – explained
- Motherboard form factors
- Baby AT (BAT) Motherboard Form Factor
- LPX – Low Profile eXtension motherboard form factor
- ATX form factor
- NLX – New Low profile eXtended – form factor for motherboards
- Micro ATX motherboard form factor
- FlexATX motherboard form factor
- BTX – Balanced Technology eXtended – Motherboard Form Factor
- Riser architectures for motherboards
- CPU interfaces – motherboard slots and sockets for AMD and Intel processors
I thought the memory slots were on the riser card??