In the early 1990s, the rapid growth of mobile computing drove the development of smaller, lighter, and more portable tools for information processing. One of the most exciting of these innovations was PC Card technology. The power and versatility of PC Cards quickly made them standard equipment in mobile computers. The rapid development and worldwide adoption of PC Card technology has been due in large part to the standards efforts of the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA).
First released in 1990, the PC Card Standard defines a 68-pin interface between the peripheral card and the socket into which it gets inserted. It defines three standard PC Card form factors, called Type I, Type II and Type III. The only difference between the card types is thickness, this being 3.3, 5.0, and 10.5 millimetres for Type I, Type II, and Type III cards respectively. Because they differ only in thickness, a thinner card can be used in a thicker slot, but a thicker card can not be used in a thinner slot.
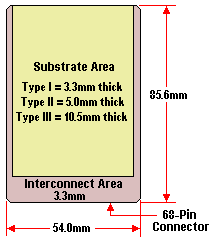
The card types each have features that fit the needs of different applications. Type I PC Cards are typically used for memory devices such as RAM, FLASH and SRAM cards. Type II PC Cards are typically used for I/O devices such as data/fax modems, LANs, and mass storage devices. Type III PC Cards are used for devices whose components are thicker, such as rotating mass storage devices. Extended cards allow the addition of components that must remain outside the system for proper operation, such as antennas for wireless applications.
In addition to electrical and physical specifications, the PC Card Standard defines a software architecture to provide plug and play capability across the widest range of products. This software is made up of Socket Services and Card Services, and it is these that allow for interoperability of PC Cards. Socket Services is a BIOS-level software layer that isolates PC Card software from the system hardware and detects the insertion and removal of PC Cards. Card Services describes an Application Programming Interface (API) which allows PC Cards and sockets to be shared by multiple clients – devices drivers, configuration utilities or application programs. It manages the automatic allocation of system resources such as memory and interrupts once Socket Services detects that a card has been inserted.
Derived from the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Local Bus signalling protocol, CardBus is the 32-bit version of PC Card technology. Enabled in the February 1995 release of the PC Card Standard, CardBus features and capabilities include 32-bits of address and data, 33MHz operation and busmaster operation.
A number of new expansion interfaces have emerged since the PC Card standard, facilitating the connection peripherals, addition of memory or provision of network connectivity. These operate in similar fashion to the PC Card format, each interface accommodating a specific type of card that is inserted into the interface. (For more information on memory expansions see the PCTechGuide section on portable RAM.)
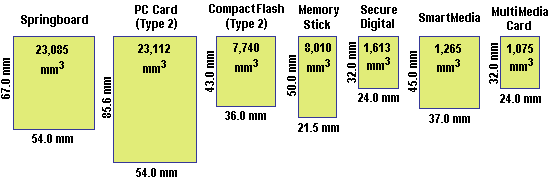
- Springboard: A proprietary interface designed by Handspring for their Visor family (Palm platform) of devices. This has the largest physical volume of the peripheral cards. It also provides the highest data transfer rate, because it allows attached I/O devices to connect directly to the processor bus. It can accommodate a separate battery to support higher power functions.
- CompactFlash: An industry-standard expansion interface for portable devices. It is widely supported, and although the CompactFlash card size is relatively small, it provides enough room to implement many functions. A popular interface for adding memory to digital cameras and portable MP3 players. In addition, serial ports, modems, Ethernet cards, cellular network attachments, and Global Positioning System (GPS) devices are implemented on CompactFlash cards. Because of this wide support, the interface is expected to be supported by many devices in the future.
- SmartMedia: The proprietary design currently manufactured by Toshiba and Samsung. Toshiba has trademarked the name, but has made the specification available for free to the industry in the hope of creating a de facto standard. Not all SmartMedia cards are interchangeable. Some require 5.0 volts from the connecting PDA, some use 3.3 volts, and others can adapt to either voltage. The voltage of the card must be matched to the voltage of the specific portable device.
- Memory Stick: Developed by Sony and Fujitsu, the Memory Stick media are relatively small and, thus, accommodate relatively few functions. Its most common use is as a memory platform. There is a Memory Stick format supported by the music industry called Magic Gate. Magic Gate supports the Secure Digital Music Initiative (SDMI) specification designed to eliminate illegal copying and distribution of copyrighted content over the Internet. Sony is driving this interface to become an industry standard, and it appears in various consumer devices such as cameras and portable MP3 players.
- MultiMediaCard: Created by joint agreement between Siemans, Hitachi, and SanDisk, the MultiMediaCard is the size of a postage stamp and is designed to provide a small memory storage medium for portable MP3 music players. Its small size limits its ability to support a variety of other I/O attachments.
- Secure Digital: In the summer of 1999 SanDisk and Toshiba reached an agreement to jointly specify and develop a variant of the MultiMedia Card format known as the SD Memory Card. The SD format includes unique and proprietary security functions in the card’s controller which facilitate the secure exchange of content between host devices and the card. The security level has been designed to comply with both current and future SDMI portable device requirements. SD interfaces have the advantage of also being able to accept a MultiMediaCard.
The card sizes for these interfaces vary, the smaller cards typically being used for memory expansion, the larger cards’ greater physical volume allowing the accommodation of additional functions:
Because of its size and power requirements, the PC Card hardware interface is not integrated into PDA devices. Instead, it is implemented in an optional sled device that attaches to the device. Because PC Card slots are so ubiquitous on portable computers, PC Cards have been developed that act as adapters for other smaller expansion cards. For example, a PC Card-to-CompactFlash adapter card allows a CompactFlash card to be inserted into the PC Card. Similar adapters have been developed for Memory Stick, MultiMediaCard, Secure Digital and SmartMedia cards. These adapters can be inserted into a PC Card slot on a portable computer and used to transfer data between the handheld and portable computers.
Most mobile devices have infrared ports, which implement the Infrared Data Association (IrDA) standard. The port can be used to connect to a desktop or portable PC to allow synchronisation of calendars, e-mail, contact lists, and other personal data or connect to cell phones, printers, and other infrared devices. As Bluetooth personal area network (PAN) technology becomes more prevalent, it is expected to replace IrDA ports on handheld devices. Alternatively, cable connection via a Universal Serial Bus (USB) or serial port may be used for this purpose. In the case of PDAs, the entire device can be inserted into a cradle that provides a USB or serial connection to a desktop, a portable PC, or to USB or serial devices.
- Flat panel displays for mobile computers – laptops, notebooks and netbooks
- Battery technology for mobile computers – laptops, notebooks and webbooks
- Laptop, notebook and netbook expansion devices
- Expansion interfaces for laptops, notebooks and other mobile computers
- DynaSheet
- External keyboards for mobile computers.
- USB On-The-Go – USB technology for PDAs and mobile phones
- Guide to Kensington Slot (K-lock, Kensington Lock, Universal Security Lock) mobile device security