In older file system architectures, if a file could not be stored contiguously, it could not be saved to the disk. Newer architectures intentionally divide files into multiple pieces so as to make more efficient use of disk storage space.
Since files are constantly being written, deleted, and resized, fragmentation is a natural and ongoing occurrence. However, it is also one that has significant performance implications. When a file is spread out over several locations, it takes longer to read and write. In fact, the effects of fragmentation can be more widespread than that, causing long boot times, random crashes and system freeze-ups.
Defragmentation is a time-consuming process, the more so the greater the extent of fragmentation. It is therefore important to terminate any programs, including those running in the background like firewalls and anti-virus programs – before starting the defragmentation process. Failure to do so will mean that it is constantly interrupted, adversely impacting the time the process takes possibly to the extent of it failing to complete.
The following describes how to defragment your hard drive using Windows XP’s disk defragmentation program, which is a free built in component of the operating system.
Note that you cannot defragment a hard disk that is completely full, and that the less free space there is, the longer defragmentation will take. This is because the defragmentation utility need some room in which to temporarily store fragments as it reassemble files.
If your hard disk is relatively full, it is therefore good practice to run Disk Cleanup before attempting to defragment a drive.
Launch the Defragmenter Tool, either via …
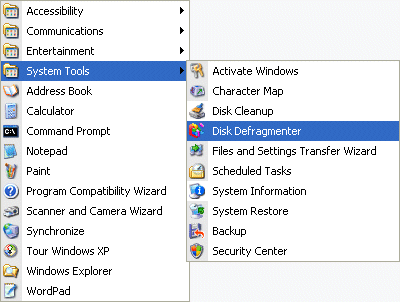
Start > Programs > Accessories > System Tools …
… or by double-clicking My Computer, right-clicking any hard disk drive, clicking Properties …
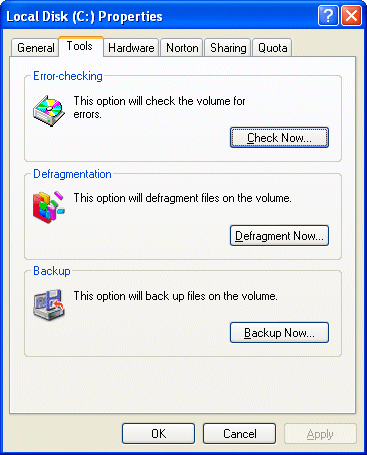
… and selecting to Tools tab.
The resulting display will list your hard disk drives, showing the capacity and amount of free space for each.
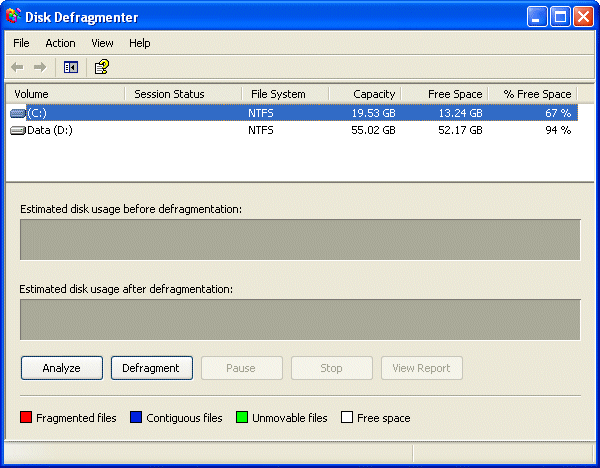
Select the drive you want to defragment and click Analyse.
The drive is scanned and a visual representation of the degree to which it is fragmented displayed.
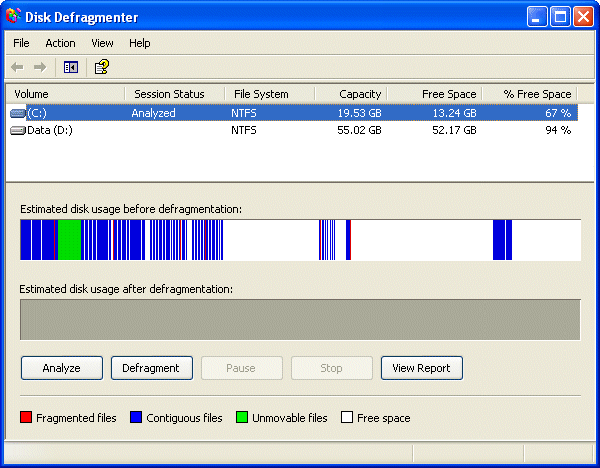
Depending on the the results of the analysis, you will be advised as to whether of not the volume should be defragmented.
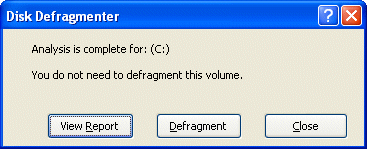
Even if it’s not strictly necessary, you can choose to Defragment.
The length of time the defragmentation takes will depend on the size of the drive, the degree to which it’s fragmented and the amount of free space it has. Be prepared to to allow it to run for several hours, if necessary.
The dialogue box will indicate when the process is complete …
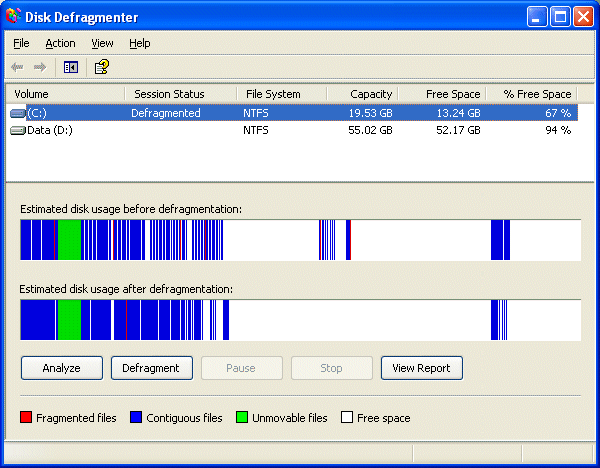
… and give a visual representation of the now defragmented drive.
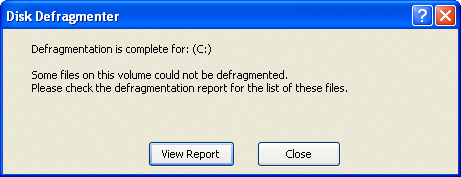
Click View Report …
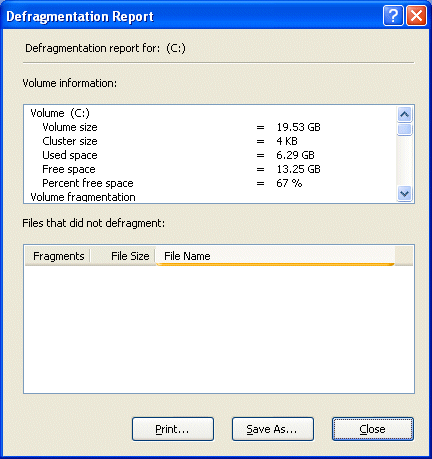
… to see a defragmentation report.
While some people address the issue of the time it takes to run defragmentation by scheduling it to be run overnight, others choose to ensure that it is not interrupted by other programs by running it in a completely clean environment, either by carrying out the process either following a clean boot or with Windows in Safe Mode.
(Refer the following associated tutorials://
- HOW TO SCHEDULE A PROGRAM USING TASK SCHEDULER
- HOW TO PERFORM A CLEAN BOOT IN WINDOWS XP
- HOW TO ADD SAFE MODE TO THE BOOT LOADER MENU.)
Relevant Microsoft Knowledge Base Articles
- 314848:// How to Defragment Your Disk Drive Volumes in Windows XP
- 555098:// How to Automate Disk Defragmenter Using Task Scheduler Tool in Windows XP
- 124917:// How Disk Defragmenter Reports Fragmentation
- 283080:// Description of the New Command Line Defrag.exe Included with Windows XP
- 227463:// Disk Defragmenter Limitations in Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003
- 186978:// Drive’s Contents Have Changed:// Restarting… Message When You Use the Disk Defragmenter Tool
- 218160:// Disk Defragmenter Hangs After Choosing Disk to Defragment
- 137113:// Disk Defragmenter Restarts Continually with Find Fast
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tools Windows XP Resource Kit