In January 2006, Intel introduced the revolutionary Intel Centrino Duo Mobile Technology platform (formerly codenamed Napa), the third generation of the company’s Centrino mobile processor technology bundle. Facilitating a whole new generation of thin and light notebook PCs, the following three next generation components will together enable future Centrino Duo laptops to surpass both the performance and battery life of previous generation Centrino platforms:
- Intel Core Duo Processor
- Mobile Intel 945 Express Chipset Family
- Intel PRO/Wireless 3945ABG Network Connection.
The Intel Core Duo processor (previously codenamed Yonah) is Intel’s first mobile dual-core processor built on the company’s next generation 65 nm process technology. This has enabled a pair of Yonah cores to be fit onto a die only slightly larger than the previous Dothan-cored Pentium M (90mm2 compared to 84mm2 for the older part). The relatively small increase in die size and total transistor count (up around 11 million to approaching 152 million) is largely explained by the fact that most of the area of the die is taken up by the same 2MB of Level 2 cache.
In addition to the new mobile dual-core architecture, the Intel Core Processor includes several innovative features. These include a number of changes which together eliminate limitations that have restricted the Pentium M’s multimedia performance relative to that of NetBurst architecture-based chips. Referred to a Digital Media Boost, these include instruction optimisations and performance enhancements for existing Streaming SIMD Extensions 2 (SSE2), 13 new Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSE3) instructions and enhancements to floating point instruction decoding performance that will allow multiple SSE instructions to be handled in parallel.
Another new feature is a shared 2MB L2 cache which enables an active execution core to access the full 2MB cache when the other execution core is idle. Dubbed Smart Cache, this uses dynamic cache allocation across both cores to enhance performance and reduce cache under-utilisation and misses. Efficient data sharing between both cores minimises FSB traffic and reduces cache coherency complexity and the processor’s enhanced Data Pre-fetch Logic speculatively fetches data to the L2 cache before cache requests occur, thereby reducing bus cycle penalties.
In the past the design of mobile processing platforms have required a trade off between performance and battery life. In the case of the Core Duo, the design goal was breakthrough performance while at the same time optimizing energy efficiency and enabling longer battery life. The result is that each of the CPU’s execution cores is able to independently and dynamically transition to Halt, Stop Clock, and Deep Sleep low-power states, so that if only one core is being utilised, the second core can still enter an idle state to help save power. Moreover, Dynamic Power Co-ordination also enables co-ordinated transitions to Deeper Sleep and an Enhanced Deeper Sleep mode, for example when the Smart Cache dynamically flushes the cache to system memory during periods of inactivity.
The Mobile Intel 945 Express Chipset Family is the next generation Intel Hub Architecture for notebook PCs using Intel Centrino Duo Mobile Technology. As with previous Centrino chipsets, there are three variants: the 945PM is the plain mobile chipset, the 945GM adds integrated graphics and the 945GMS is the ultra-low voltage chipset with integrated graphics.
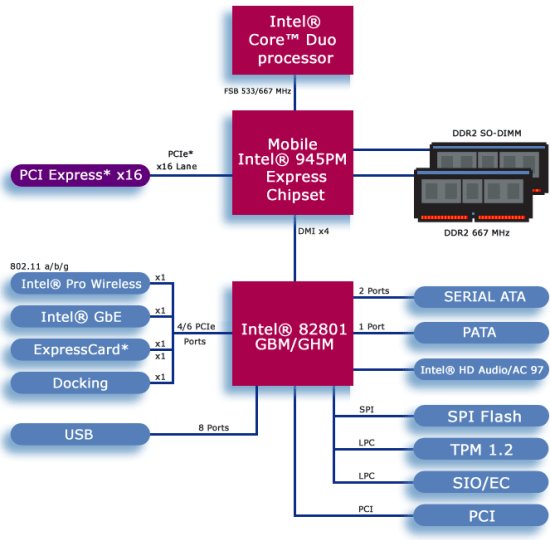
The features of the 945PM chipset include:
| Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| 667 MHz Front Side Bus | Supports Intel Core Duo and Intel Core Solo processors with up to 25% faster data transfer rate compared to the previous generation bus speed. |
| PCI Express* x16 Interface | Delivers greater than 3.5 times the bandwidth over the traditional AGP interface and supports the latest high-performance graphics cards. |
| PCI Express* x1 Interface | Offers up to 3.5 times the bandwidth over traditional PCI architecture, delivering faster access to peripheral devices and networking. |
| Intel High Definition (HD) Audio | Integrated audio support enables premium sound and delivers advanced features such as multiple audio streams and jack re-tasking. |
| Intel Matrix Storage Technology | Enables enhanced performance, power management and data protection for the storage subsystem. |
| Dual-channel DDR2 667MHz Memory Support | Up to 10.7 GBps of bandwidth and up to 4GB memory addressability, for faster system responsiveness. |
| Integrated high speed USB 2.0 | Support for 8 USB 2.0 peripherals for maximum 40x faster data transfer and backward compatible to support USB 1.1 devices. |
The 945GM and GMS variants’ integrated graphics is provided by the new Graphics Media Accelerator 950 (GMA 950) graphics engine. Graphics require dedicated memory and processing, and applications have divergent memory needs. Some applications, such as e-mail and Internet browsing, require very little graphics memory. Others, such as games, require more. Intel GMA 950 graphics support both of these demand levels through a unique intelligent memory management scheme called Dynamic Video Memory Technology (DVMT). DVMT handles these diverse applications by providing the maximum availability of system memory for general computer usage, while supplying additional graphics memory when a 3D-intensive application requests it.
Intel GMA 950 also supports Dual Independent Display technology. When an optional adapter card is installed, this capability allows two separate displays to be connected to the system at the same time. One way to use this capability is to create a larger desktop work surface spanning multiple displays. Intel GMA 950 graphics also supports Media Expansion Cards, which enable dual TV tuning and digital display connectors such as DVI and TV-Out in a single card solution.
As with previous version of Centrino, the Centrino Duo platform specifies an Intel wireless card, in this case Intel PRO/Wireless 3945ABG Network Connection adapter. Compatible with all three commonly used wireless standards, 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g, this operates at 5 GHz or 2.4 GHz frequency at speeds of up to 54 Mbit/sec. Supporting enhanced features that make applications more aware, connected, and responsive, enabling mobile PCs to deliver a better on-the-go end-user experience, the 3945ABG is also available in a smaller PCIe mini-card form factor, facilitating lighter and thinner notebooks.
Access points usually serve bandwidth on a first-come, first-served basis. This presents problems for high bandwidth applications such as VoIP and media streaming. The 3945ABG provides a solution via version 10 of the Intel PROSet/Wireless software, which allows such applications to prioritise and reserve bandwidth using 802.11e QoS parameters. In addition, an intelligent access point selection feature allows load balancing of traffic across multiple access points, which helps increase overall bandwidth capacity, thereby potentially enhancing data, voice and video throughput.
- Mobile Intel Pentium MMX technology guide
- Illustrated Intel Pentium Tillamook CPU technology guide
- Intel Mobile Pentium II technology guide
- Illustrated guide to Cyrix’s MediaGXi technology
- Guide to Intel’s Mobile Celeron CPU
- AMD Mobile K6 CPU Technology Guide
- Intel Mobile Pentium III and Tualatin Pentium III-M Guide
- Speedstep – Intel’s mobile CPU dynamic power management architecture
- Crusoe – Transmeta Corps’ x86 compatible VLIW mobile CPU
- Intel XScale – Pocket PC dynamic power management
- AMD’s Mobile Duron technology guide
- Mobile AMD Athlon 4 technology guide
- Guide to PowerNow! – AMD’s dynamic power management technology
- Intel Pentium 4-M mobile CPU guide
- Intel Centrino mobile computer platform
- Intel Sonomo improves wireless integration in mobile devices
- Illustrated Intel Centrino Duo technology guide
- Merom – Intel’s mobile Core 2 Duo CPU technology guide