While scanners provide an effective means of capturing colour images, that's often just the beginning. Once a photograph, for example, has been digitised, its appearance can be dramatically altered by use of a bitmap editor or paint … [Read more...]
OCR Technology
When a page of text is scanned into a PC, it is stored as an electronic file made up of tiny dots, or pixels; it is not seen by the computer as text, but rather, as a picture of text'. Word processors are not capable of editing bitmap images. In order to turn the group of pixels into editable words, … [Read more...]
Color Calibration
One of the frustrations of using a desktop scanner is that a scanned image can look different on screen than it does when printed, and both can vary quite a bit from the original. The solution to this problem is a colour calibration (or colour … [Read more...]
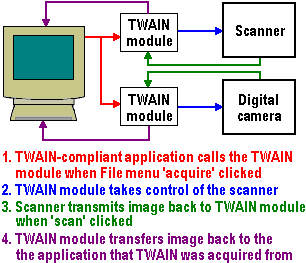
TWAIN Drivers
Surprisingly TWAIN is not an acronym, but a very important standard in image acquisition, developed by Hewlett-Packard, Kodak, Aldus, Logitech and Caere which specifies how image acquisition devices such as scanners, digital cameras and other … [Read more...]
Scanner File Formats
The format in which a scanned image is saved can have a significant effect on file size - and file size is an important consideration when doing some image and document scanning, since the high resolutions supported by many modern scanners can result in the creation of image files as large as 30MB … [Read more...]
Scan Modes
PCs represent pictures in a variety of ways - the most common methods being are line art, halftone, greyscale, and colour: Line art is the smallest of all the image formats. Since only black and white information is stored, the computer … [Read more...]
Dynamic Range Scanners
Dynamic range is somewhat similar to bit-depth in that it measures how wide a range of tones the scanner can record. It is a function of the scanner's analogue-to-digital converter - along with the purity of the … [Read more...]
Bit-Depth Printers
When a scanner converts something into digital form, it looks at the image pixel by pixel and records what it sees. That part of the process is simple enough, but different scanners record different amounts of information about each pixel. How much … [Read more...]
Color Scanners
Colour scanners have three light sources, one for each of red, green and blue primary. Some scanning heads contain a single fluorescent tube with three filtered CCDs, while others have three coloured tubes and a single CCD. The former … [Read more...]
Scanner Interpolation
Scanners typically offer resolutions of 2,400dpi, 4,800dpi and 9,600dpi. Its important to realise that scanners simply aren't capable of picking up this level of detail. The actual optical resolution of the CCDs in most … [Read more...]