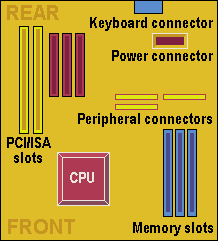
The Baby AT (BAT) format reduced the dimensions of the motherboard to a typical 9in wide by 10in long, and BAT motherboards are generally characterised by their shape, an AT-style keyboard connector soldered to the board and serial and parallel … [Read more...]
Motherboard form factors
Early PCs used the AT form factor and 12in wide motherboards. The sheer size of an AT motherboard caused problems for upgrading PCs and did not allow use of the increasingly popular slimline desktop cases. These problems were largely addressed by the smaller version of the full AT form factor, … [Read more...]
EFI – Extensible Firmware Interface – explained
The BIOS has evolved very little since the birth of the PC in 1981, remaining a chunk of hand-crafted assembly language code most users know only for the series of arcane configuration and test messages fleetingly displayed when they turn on their PC. Intel first signalled that all … [Read more...]
CMOS – complementary metal oxide silicon – RAM chips on motherboards
Motherboards also include a separate block of memory made from very low power consumption CMOS (complementary metal oxide silicon) RAM chips, which is kept alive by a battery even when the PC's power is off. This is used to store basic information about the PC's configuration: number and … [Read more...]
BIOS – What motherboard BIOS does for a PC
All motherboards include a small block of Read Only Memory (ROM) which is separate from the main system memory used for loading and running software. The BIOS will most likely be stored in a 32-pin chip, which can typically be identified by a silver or gold sticker that shows the name … [Read more...]
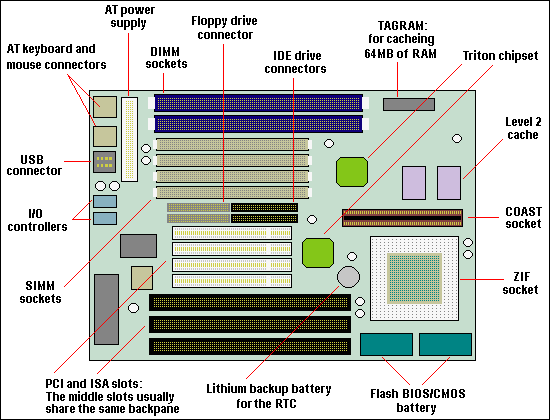
Evolution of the motherboard
The original PC motherboard had a minimum of integrated devices, just ports for a keyboard and a cassette deck (for storage). Everything else, including a display adapter and floppy or hard disk controllers, were add-in components, connected via expansion slots. Over time, more devices were … [Read more...]