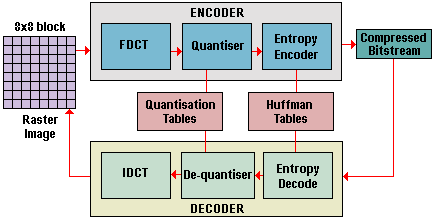
Video compression is the art of throwing as much data away as possible without it showing. Video compression methods tend to be lossy - that is, what comes out after decoding isn't identical to what was originally encoded. By cutting … [Read more...]
Digital Video Performance Requirements
Digital video relies primarily on hard disk power and size, and the important characteristic is sustained data throughput in a real-world environment. Video files can be huge and therefore require a hard disk drive to sustain high rates of data … [Read more...]
Digital Video Editing
Broadly speaking, there are two types of video editing. One involves editing directly from one tape to another and is called linear editing. The other requires that the sequences to be edited are transferred to hard disk, edited, and then transferred back to tape. This method is referred to as … [Read more...]
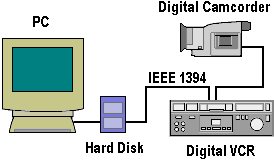
Digital Video Camcorders
As recently as the first half of the 1990s few would have dreamed that before long camcorders would be viewed as a PC peripheral and that video editing would have become one of the fastest growing PC applications. All that changed with the … [Read more...]
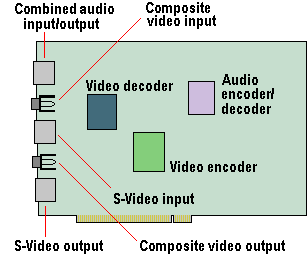
Capturing Digital Video
The digitisation of the analogue TV signal is performed by a video capture card which converts each frame into a series of bitmapped images to be displayed and manipulated on the PC. This takes one horizontal line at a time and, for the PAL … [Read more...]
Digital Video Fundimentals
Understanding what digital video is first requires an understanding of its ancestor - broadcast television or analogue video. The invention of radio demonstrated that sound waves can be converted into electromagnetic waves and transmitted … [Read more...]
MPEG Video
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) have defined a series of standards for compressing motion video and audio signals using DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) compression which provide a common world language for high-quality digital video. … [Read more...]
M-JPEG
JPEG is a well-known standard for compressing stills. Unlike MPEG, M-JPEG compresses and stores every frame rather than only the differences between one frame and the next. Thus it requires more space than MPEG, but it is more efficient when … [Read more...]
Cinepak technology
Cinepak is another asymmetric video compressor, developed jointly by Apple and SuperMac (a company later acquired by Radius). The format outputs 320x240 (quarter screen) at 15 fps with good quality, at a data rate that even slow … [Read more...]