The P6 microarchitecture is the sixth generation of Intel's x86 processor architecture, first implemented in the design of the Pentium Pro CPU, introduced in 1995 as the successor to the original P5 Pentium design. The Pentium Pro introduced several unique architectural features that had … [Read more...]
Pentium P5 microarchitecture – superscalar and 64 bit data
First introduced in 1993, the Pentium was the successor to Intel's 486 line of CPUs and the defining processor of the fifth generation. The original Pentium microprocessor had the internal code name P5, and was a pipelined in-order superscalar microprocessor, produced using a 0.8 µm … [Read more...]
IA-32 (Intel Architecture 32 ) – base instruction set for 32 bit processors
IA-32 - sometimes generically called x86-32 - is the instruction set architecture of Intel\'s family of 32-bit microprocessors; previous microprocessor architecture had been 16-bit. It was introduced in the Intel\'s third generation 80386SX and DX processors in 1985. In fact, the 386SX was … [Read more...]
Microprocessor Evolution
The 4004 CPU was the forerunner of all of today's Intel offerings and, to date, all PC processors have been based on the original Intel designs. The first chip used in an IBM PC was Intel's 8088. This was not, at the time it was chosen, the best available CPU, in fact Intel's own 8086 … [Read more...]
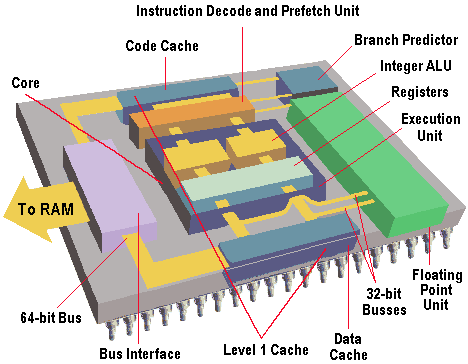
Basic structure of a Pentium microprocessor
A Pentium processor's major functional components are: Core: The heart of a Pentium is the execution unit. The Pentium has two parallel integer pipelines enabling it to read, interpret, execute and despatch two instructions simultaneously. Branch Predictor: The branch prediction unit tries … [Read more...]
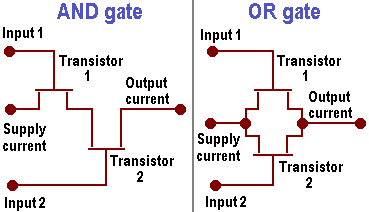
Principles of CPU architecture – logic gates, MOSFETS and voltage
The underlying principles of all computer processors are the same. Fundamentally, they all take signals in the form of 0s and 1s (thus binary signals), manipulate them according to a set of instructions, and produce output in the form of 0s and 1s. The voltage on the line at the time a signal is … [Read more...]