Chkdsk.exe is a utility which verifies the logical integrity of a file system. In the event of the utility encountering logical inconsistencies in file system data, it will perform the necessary actions to repair the file system data.
The equivalent utility in earlier versions of Windows was referred to as ScanDisk.
The following describes how to perform error-checking of a hard drive under Windows XP.
Launch disk error checking by double-clicking My Computer, right-clicking the hard disk drive you want to have checked, clicking Properties …
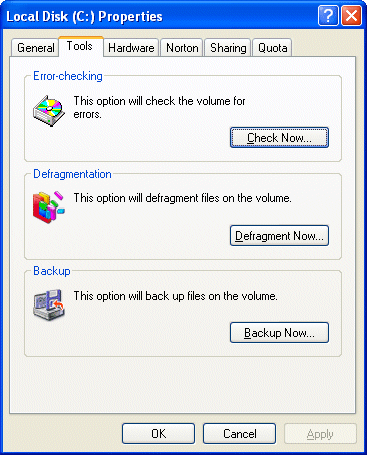
… and selecting the Tools tab.
Click Check Now.
The Windows 98 equivalent to the Windows XP disk error-checking program (chkdsk.exe) is the ScanDisk utility, accessed via Start > Programs > Accessories > System Tools.
This provides options for performing either a standard or thorough test of the specified disk volume. The former checks files and folders for errors, while the latter additionally scans the disk for physical errors.
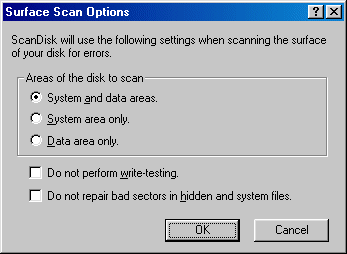
Select the required option for the areas of the disk to be scanned. ScanDisk usually cannot repair errors in the system area of a disk. If such errors exist, your disk probably needs to be replaced.
Specify whether or not you want ScanDisk to verify that sectors can be read from and written to, and/or have the utility repair hidden and system files on your disk.
A dialogue box showing the Check disk options is displayed.
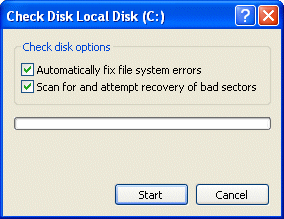
Select the options as appropriate and click Start.
If either of the Check disk options are selected, you’ll be notified that the check cannot be performed immediately, and offered the opportunity to schedule this to occur the next time your system is booted.
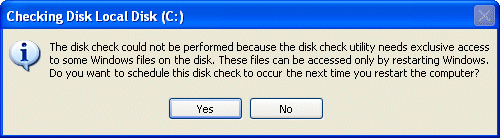
Click Yes to so schedule the disk check.
The next time you start your system, the chkdsk.exe utility will be run prior to Windows being loaded, examining all the metadata on the volume in five separate phases:
- Phase 1: Verifying file data
- Phase 2: Verifying security descriptors
- Phase 3: Verifying indexes
- Phase 4: Verifying files
- Phase 5: Verifying free space
Metadata is data about data.
Metadata is the file system overhead, so to speak, that keeps track of information about all of the files that are stored on the disk volume. It includes information about what allocation units make up the data for a given file, what allocation units are free, what allocation units contain bad sectors, and so on.
Contrast the actual data that the file contains, which is referred to as user data.
When the utility finishes, Windows will continue to load as per a normal system start-up.
Relevant Microsoft Knowledge Base Articles
- 315265: How to Perform Disk Error Checking in Windows XP
- 316506: Chkdsk Runs Each Time That You Start Your Computer
- 831426: Chkdsk.exe or Autochk.exe starts when you try to shut down or restart your computer
- 314835: An explanation of the new /C and /I Switches that are available to use with Chkdsk.exe
- 186365: Description of ScanDisk for Windows (Scandskw.exe) in Windows 98/Me
- 287914: List of Articles About the ScanDisk Tool
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tools Windows XP Resource Kit
Not the same thing. Defrag is different. Don’t be a dummy.
I was searching for a post like this, to perform error-check from days together. I don’t the entire process and this blog has taught me the entire process. Now I find error-checking to be very simple and easy. Thanks for sharing such informative post.