Since 1998, when the fashion was established by Creative Technology’s highly successful SoundBlaster Live! card, many soundcards have enhanced connectivity via use an additional I/O card, which fills a 5.25in drive blanking plate and is connected to the main card using a short ribbon cable. In its original incarnation the card used a daughter card in addition to the breakout I/O card. In subsequent versions of the daughter card disappeared and the breakout card became a fully-fledged 5.25in drive bay device, which Creative referred to as the Live!Drive.
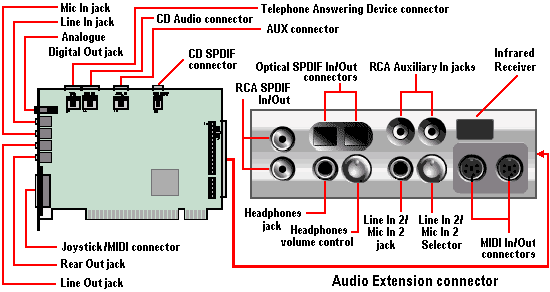
The Platinum 5.1 version of Creative’s card – which first appeared towards the end of 2000 – sported the following jacks and connectors:
- Analogue/Digital Out jack: 6-channel or compressed Dolby AC-3 SPDIF output for connection to external digital devices or digital speaker systems; also supports centre and subwoofer analogue channels for connection to 5.1 analogue speaker systems
- Line In jack: Connects to an external device such as cassette, DAT or MiniDisc player
- Microphone In jack: Connects to an external microphone for voice input
- Line Out jack: Connects to powered speakers or an external amplifier for audio output; also supports headphones
- Rear Out jack: Connects to powered speakers or an external amplifier for audio output
- Joystick/MIDI connector: Connects to a joystick or a MIDI device; can be adapted to connect to both simultaneously
- CD/SPDIF connector: Connects to the SPDIF (digital audio) output, where available, on a CD-ROM or DVD-ROM drive
- AUX connector: Connects to internal audio sources such as TV tuner, MPEG or other similar cards
- CD Audio connector: Connects to the analogue audio output on a CD-ROM or DVD-ROM using a CD audio cable
- Telephone Answering Device connector: Provide a mono connection from a standard voice modem and transmits microphone signals to the modem
- Audio Extension (Digital I/O) connector: Connects to the Digital I/O card or Live! Drive
and the front panel of the Live!Drive IR device provided the following connectivity:
- RCA SPDIF In/Out jacks: Connects to digital audio devices such as DAT and MiniDisc recorders
- 1/4 Headphones jack: Connects to a pair of high-quality headphones; speaker output is muted
- Headphone volume: Controls the headphones output volume
- 1/4 Line In 2/Mic In 2 jack: Connects to a high-quality dynamic microphone, studio mics or audio device such as an electric guitar, DAT or MiniDisc player
- Line In 2/Mic In 2 selector: Control the selection of either Line In2 or Mic In 2 and the microphone gain
- MIDI In/Out connectors: Connects to MIDI devices via a Mini DIN-to-Standard DIN cable
- Infrared Receiver: Allows control of the PC via a remote control
- RCA Auxiliary In jacks: Connects to consumer electronics equipment such as VCR, TV and CD player
- Optical SPDIF In/Out connectors: Connects to digital audio devices such as DAT and MiniDisc recorders.
Other sound card manufacturers were quick to adopt the idea of a separate I/O connector module. There were a number of variations on the theme. Some were housed in an internal drive bay like the Live!Drive, others were external units, some of which were designed to act as USB hubs.
- How Do Computers Make Pictures?
- Graphic Card Resolution
- Graphic Card Colour Depth
- Graphic Card Components
- Graphic Card Memory
- Graphic Card Driver Software
- 3d Accelerated Graphic Cards
- Graphic Card Geometry
- 3D Rendering
- FSAA Graphic Card Technology
- Digital Graphic Cards
- DVI Graphic Cards
- HDCP Technology
- Graphic Card HDMI Ports
- Graphic Card Display Port
- Unified Display Special Interest Group
- DirectX
- OpenGL technology
- Direct3D
- Talisman
- Fahrenheit Graphic Cards
- SLI Technology
- CrossFire Graphic Cards