Despite the floptical’s failure to oust the traditional floppy disk, for several years it appeared likely that optical drives, which read/wrote data with lasers which are far more precise than the drive heads on a traditional hard drive, were destined to replace magnetic disk technology.
WORM (Write Once, Read Many) storage had emerged in the late 1980s and was popular with large institutions for the archiving of high volume, sensitive data. When data is written to a WORM drive, physical marks are made on the media surface by a low-powered laser and since these marks are permanent, they cannot be erased.
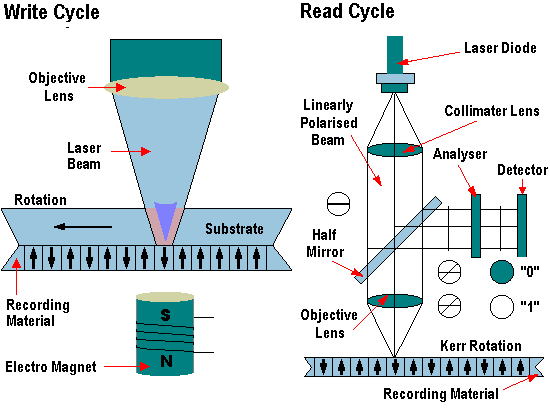
Rewritable, or erasable, optical disk drives followed, providing the same high capacities as those provided by WORM or CD-ROM devices. However, despite the significant improvements made by recent optical technologies, performance continued to lag that of hard disk devices. On the plus side optical drives offered several advantages. Their storage medium is rugged, easily transportable and immune from head crashes and the kind of data loss caused by adverse environmental factors.
The result is that the relative advantages of the two types of system make them complementary rather than competitive – optical drives offering security, magnetic drives real-time performance. The development of the CD/DVD technologies to include recordable and rewritable formats has had a dramatic impact in the removable storage arena and compatibility is an important and unique advantage of the resulting family of products. Today’s market is large enough to accommodate a number of different technologies offering a wide range of storage capacities.
The predominant are:
- magnetic disk
- magneto-optical
- phase-change
At time of writing, the resulting range of capacities can be categorized as follows:
- floppy replacements (100MB to 150MB)
- super-floppies (200MB to 300MB)
- hard disk complement (500MB to 1GB)
- removable hard disks (1GB plus)
You can find out much more about various computer storage media in the main PCTechGuide section on PC data storage, including CD-ROM, DVD, and Blu-ray.
- Floppy Disk Data Storage
- Optical drives – WORM Write Once Read Many technology
- Magnetic Disk Technology
- Magneto-optical drives – MO technology
- LIMDOW Data Storage
- MO Media
- OSD Data Storage Technology
- Florescent Disc Technology
- Phase Change Technology
- Floppy Disc Replacements
- Super Floppies
- Hard Disk Compliment
- Tape Storage Compatibility
- Holographic Data Storage