Introduced in the late 1990s, the MicroATX is basically a smaller version of Intel’s ATX specification, intended for compact, low-cost consumer systems with limited expansion potential.
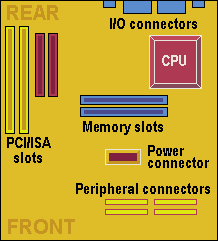
The maximum size of the board is 9.6in square, and its designed to fit into either a standard ATX case or one of the new micro-tower desktop designs. The double-decker I/O shield is the same as that on the ATX design, but there’s only provision for up to four expansion slots as opposed to the seven that ATX allows. The microATX also allows use of a smaller power supply, such as the SFX design, which is reduced in both size and power output.
- Evolution of the motherboard
- BIOS – What motherboard BIOS does for a PC
- CMOS – complementary metal oxide silicon – RAM chips on motherboards
- EFI – Extensible Firmware Interface – explained
- Motherboard form factors
- Baby AT (BAT) Motherboard Form Factor
- LPX – Low Profile eXtension motherboard form factor
- ATX form factor
- NLX – New Low profile eXtended – form factor for motherboards
- Micro ATX motherboard form factor
- FlexATX motherboard form factor
- BTX – Balanced Technology eXtended – Motherboard Form Factor
- Riser architectures for motherboards
- CPU interfaces – motherboard slots and sockets for AMD and Intel processors