The Unified Display Interface Special Interest Group (UDI SIG) was announced in December 2005, with a membership which includes Silicon Image Inc., Intel, Apple Computer, LG, Samsung and NVIDIA. The group finalised its V1.0a specification in July 2006, proposing a digital video interface that improves on the existing DVI standard at a lower implementation cost and that provides compatibility with existing HDMI and DVI displays.
UDI is specifically targeted towards the needs of computer monitor and video card manufacturers, as opposed to HDMI which is aimed at high-definition multimedia consumer electronics devices such as television monitors and DVD players. Like DVI and unlike HDMI and DisplayPort, UDI lacks audio capabilities; like HDMI, it supports the HDCP anti-piracy system. However, unlike with HDMI – for which there are no commercially available implementations that do not have HDCP keys – it is expected that its targeting of lower cost markets will mean that HDCP is less aggressively implemented with UDI.
UDI is composed of two electrical links, a UDI Data Link and a UDI Control Link. The UDI Data Link is a unidirectional high speed link used to transport the media data from source to sink. It is composed of either one or 3 differential data pairs referred to as lanes, plus a reference clock pair for the External Profile case. The data is carried on the data lanes via encoded symbols. The symbol rate is always a direct ratio of the video pixel data rate, dependent on the pixel format and lane width. UDL symbol rates can range from 25MHz to a max frequency determined by the capabilities of both the source and sink. The video pixels are RGB encoded and the colour depth can be 18, 24, 30 or 36 bits per pixel. The electrical interface is based on differential AC-coupled signals, allowing different DC bias voltages between the Source and Sink implementations and is compatible with the sink bias requirements of HDMI.
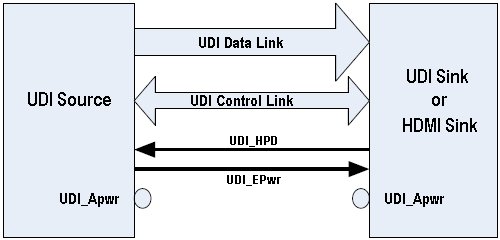
The UDI Control Link, is a bi-directional low speed link used to pass capability, control and status information. UDI Sources are expected to read the Sink’s capabilities and to deliver only the video formats that are supported by the Sink. UCL is also used by the optional HDCP technology.
The control link also includes an additional support signal, UDI_HPD, and two power lines, UDI_EPwr and UDI_APwr. The UDI_HPD signal indicates to a UDI Source that a Sink is present and provides a mechanism for the Sink to signal events to the Source. The UDI_EPwr signal provides minimal power from the Source to the Sink for reading Sink capabilities on embedded links and for compatibility with HDMI sinks on external links. On external connectors, an additional higher level of auxiliary power is provided on the UDI_APwr pin to supply operational power to an external device such as a repeater.
A UDI connector will have a single row of 22 contacts pitched 0.6 mm apart from each other, looking very similar to the Intel-initiated USB plug which has a single row with only 4 contacts. 3 of the 22 contacts will not be wired but are reserved for undetermined future upgrade possibilities. Transmit and receive plugs are slightly different, and a UDI cable will fit only one way.

The factors considered in defining the connector interface include improving signal integrity and EMI management over the HDMI connector, as well as some mechanical and form factor constraints. The receptacle connectors are so defined to accept either plugs with passive locks, or active locks (mechanical latches). The active lock feature on the plug is optional and it is users’ decision of which type plug to use. The receptacle connector is defined with two 1.1mm by 2mm (minimum) cutouts, or windows to work with the latches. It is expected that majority applications will use passive lock for cable retention. The number of passive locks is increased from 2 to 4, as compared to HDMI, to achieve a higher unmating force, which enables more applications to use the simple passive lock cable assemblies.
By the late summer of 2006, Intel Corp. had committed to sorting out the competition between the UDI and DisplayPort digital display interfaces by the end of the year.
- How Do Computers Make Pictures?
- Graphic Card Resolution
- Graphic Card Colour Depth
- Graphic Card Components
- Graphic Card Memory
- Graphic Card Driver Software
- 3d Accelerated Graphic Cards
- Graphic Card Geometry
- 3D Rendering
- FSAA Graphic Card Technology
- Digital Graphic Cards
- DVI Graphic Cards
- HDCP Technology
- Graphic Card HDMI Ports
- Graphic Card Display Port
- Unified Display Special Interest Group
- DirectX
- OpenGL technology
- Direct3D
- Talisman
- Fahrenheit Graphic Cards
- SLI Technology
- CrossFire Graphic Cards