Unveiled in October 1995, the 6×86 was the first Pentium-compatible processor to reach the market and the result of a collaboration with IBM’s Microelectronics Division. Acceptance of the 6×86 was initially slow because Cyrix priced it too high, mistakenly thinking that since the chip’s performance was comparable to Intel’s, its price could be too. Once Cyrix readjusted its sights and accepted its position as a low-cost, high-performance alternative to the Intel Pentium series, the chip made a significant impact in the budget sector of the market.
Since a 6×86 processor was capable of an equivalent level of performance to a Pentium chip at a lower clock speed, Cyrix collaborated with a number of other companies to develop an alternative to the traditional clock speed-based rating system. The resulting Processor Performance rating, or P-rating, is an application-based standardised performance measure and Cyrix processors traditionally run at a slower clock speed than their P-rating with no apparent performance degradation. For example, the P133+ runs at a clock speed of 110MHz, while the P150+ and P166+ run at 120MHz and 133MHz respectively.
The 6×86’s superior performance was due to improvements in the chip’s architecture which allowed the 6×86 to access its internal cache and registers in one clock cycle (a Pentium typically takes two or more for a cache access). Furthermore, the 6×86’s primary cache was unified, rather than comprising two separate 8KB sections for instructions and data. This unified model was able to store instructions and data in any ratio, allowing an improved cache hit rate in the region of 90%.
Indeed, the 6×86 has a number of similarities to the Pentium Pro. It’s a sixth-generation superscalar, superpipelined processor, able to fit a Pentium P54C socket (Socket 7). It contains 3.5 million transistors, initially manufactured on a 0.5 micron five-layer process. It has a 3.3v core with 5v I/O protection.
The 6×86 features, like that of the Pentium, are: superscalar architecture, 80-bit FPU, 16KB primary cache and System Management Mode (SMM). However, it has a number of important differences. The 6×86 is superpipelined, meaning there are seven, instead of five, pipeline stages (Prefetch, two Decode, two Address Generation, Execute, and Write-back) to keep information flowing faster and avoid execution stalls. Also present is Register Renaming, providing temporary data storage for instant data availability without waiting for the CPU to access the on-chip cache or system memory.
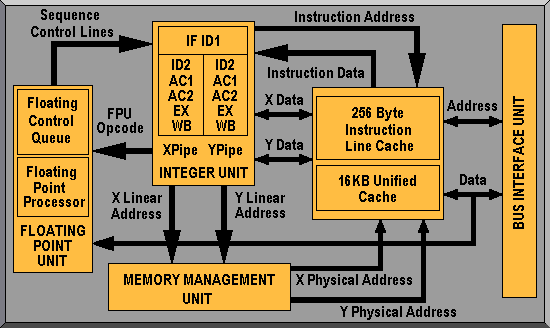
Other new features include data dependency removal, multi-branch prediction, speculative execution out-of-order completion. The presence of these architectural components prevent pipeline stalling by continually providing instruction results: predicting requirements, executing instructions a high level of accuracy and allowing faster instructions to exit the pipeline of order, without disrupting the program flow. All this boosts 6×86 performance a level beyond a similarly-clocked Pentium.
CISC Architecture
The real key to the 6×86 is its processing of code. It handles code in native mode; it fully optimises the x86 CISC instruction set. This applies to both 16- and 32-bit code. The Pentium does this, too, but by contrast a Pentium Pro requires the conversion of CISC instructions to RISC (or micro) operations before they enter the pipelines. Consequently, the 6×86 execution engine, unlike the Pentium Pro, doesn’t take a performance hit when handling 16- or 32-bit applications because no code conversion is required. The Pentium Pro, on the other hand, is known to be designed as a pure 32-bit processor and 16-bit instructions can stall considerably while in its pipeline.
All of these additional architectural features add up to one thing for the Cyrix 6×86: better performance at a lower clock speed. Compared with a Pentium on a clock-for-clock basis, the 6×86 is a more efficient chip.
However, early 6x86s in particular were plagued by a number of problems, notably overheating, poor floating-point performance and Windows NT incompatibilities. These adversely impacted the processor’s success and the 6×86’s challenge to the Pentium proved short-lived, being effectively ended by the launch of Intel’s MMX-enabled Pentiums at the start of 1997.